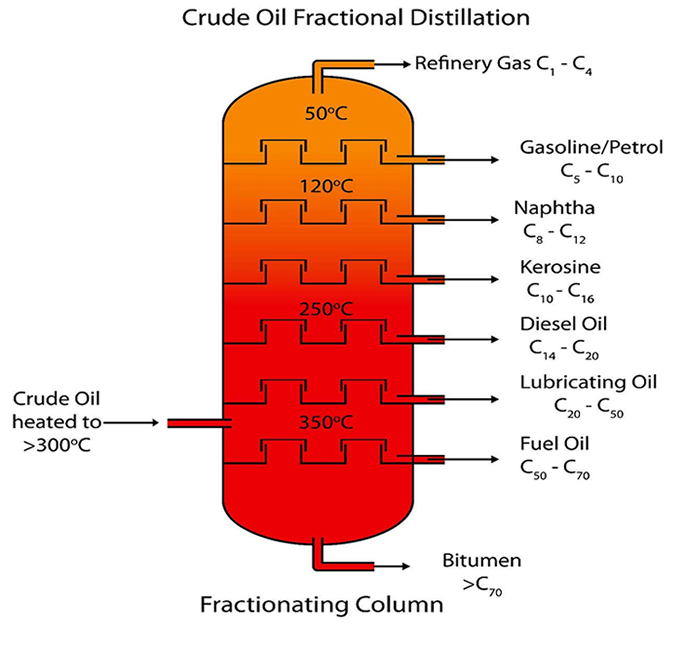
Due to the increasing need for environmental protection and increasingly stringent environmental legislation, the disposal and recycling of waste engine oil have become very important. Significant changes have taken place in waste engine oil recycling technology over the past decade. Foreign waste engine oil regeneration is mainly based on hydro refining technology, as well as new supercritical technology, membrane separation technology, molecular distillation technology, etc., while domestically, it is mainly based on small-scale acid-base refining and adsorption refining. The recovery of waste engine oil can be accomplished by the following different methods: re-purification, re-refining, and re-refining. Waste engine oil regeneration and recovery products are low-quality lubricants and fuel oils, respectively, while waste engine oil re-refining is to produce base oils of comparable quality to crude oil. In general, waste engine oil refining requires the following four steps: dewatering and degreasing, deasphalting, fractionation, and finishing.

Today we mainly introduce the solvent extraction and refining process:
The solvent refining process is still one of the current methods for producing diesel in the mainstream industry. The principle of solvent refining is to use certain organic solvents to distinguish the solubility of hydrocarbons and additives, oxidation products and sludges contained in waste lubricating oils, and to add additives, oxidation products, sludges, etc. in waste oil under certain conditions. The impurities are removed, and then the solvent is distilled off to obtain a crude product, and the crude product is purified by white clay to become a regenerated oil. In foreign countries, solvent refining has gradually changed from propane to N-methyl pyrrolidone and furfural as solvents for the refining process, and N-methyl pyrrolidone is widely used because it is superior to other solvents, It saves energy because it has the lowest toxicity and can be used at the lower agent to oil ratios. In China, we mainly study the mixture of alcohol and ketone (isopropanol, acetone, etc.)as a solvent, which can reduce the coking and scaling problems in the subsequent solvent recovery distillation process. Although the solvent refinement process has all of the above advantages, there are still some problems that cannot be solved. A disadvantage of solvent refining techniques is the dependence of the quality of the finished oil on the quality of the raw materials, as this process is a physical process and does not involve any chemical reactions. At the same time, the ratio of the agent to the oil in the refining process is high, and the use of such a solvent with certain toxicity may cause serious damage to the environment and equipment. However, the unstable price fluctuation of the N-methyl pyrrolidone solvent and the high unit price are also one of the reasons that restrict the development of the process. Although the solvent can be recycled and reused, the recovery is difficult, the recovery cost is also high, and the recovered oil sample yield is not ideal. Nowadays, domestic and foreign research has begun to study how to improve the solvent refining process. In this regard, most of them involve the addition of additives. A simple understanding of the additive technology is to add a certain amount of suitable additives in the solvent refining process in order to solve various problems that often occur in the solvent refining process, in order to obtain better refining effect. At present, most of the research on additive technology is still limited to preliminary research in the laboratory. It is still difficult to realize in the amplification experiment and industrial use. Therefore, additive technology still has great research value.